Extending Medical Aid in Dying to Incompetent Patients: A Qualitative Descriptive Study of the Attitudes of People Living with Alzheimer’s Disease in Quebec
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7202/1084452arKeywords:
euthanasia, dementia, qualitative, MAiD, incompetence, advance requestLanguage(s):
EnglishAbstract
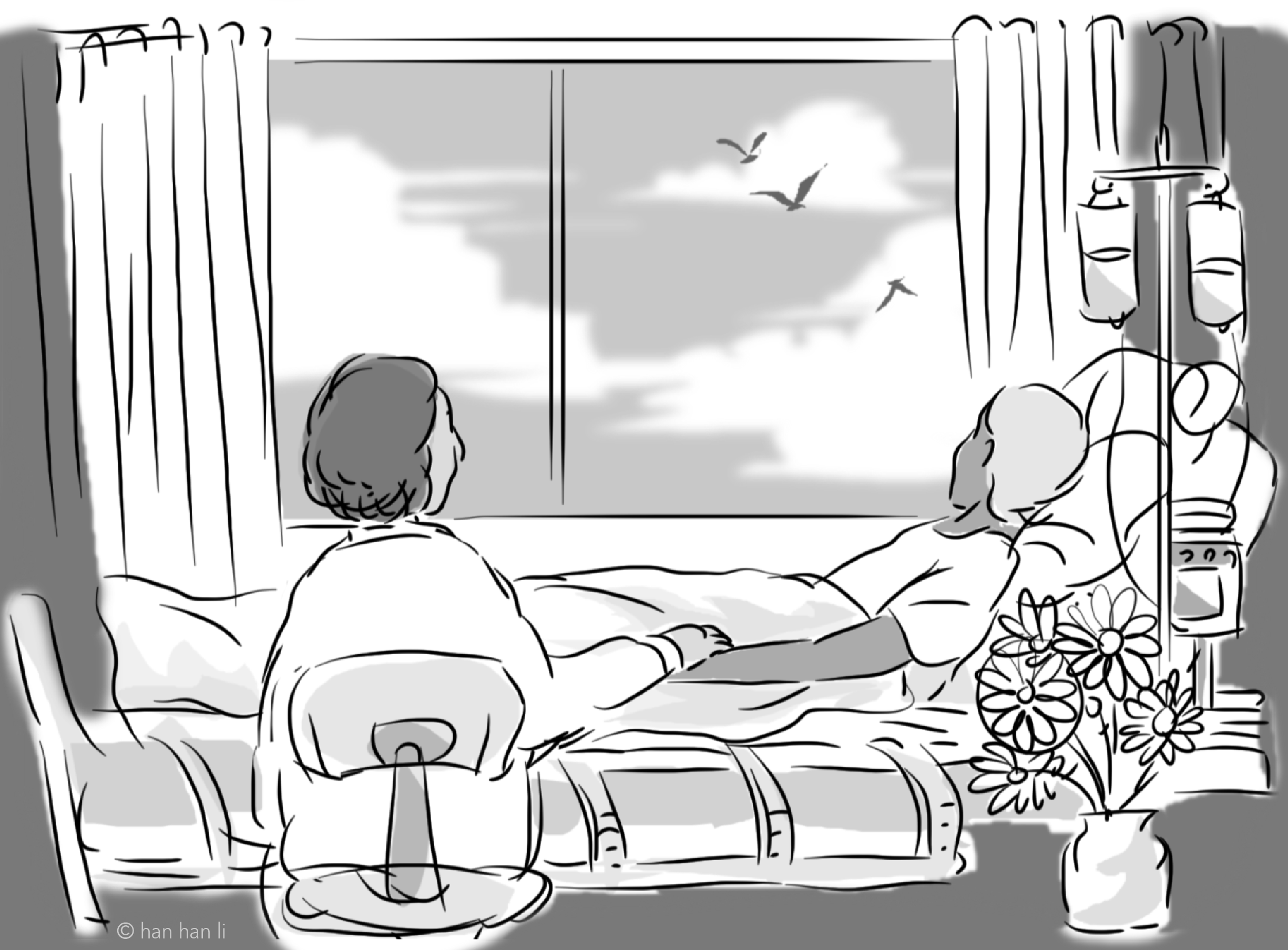
Background: In Quebec, medical aid in dying (MAiD) is legal under certain conditions. Access is currently restricted to patients who are able to consent at the time of the act, which excludes most people with dementia at an advanced stage. However, recent legislative and political developments have opened the door to an extension of the legislation that could give them access to MAiD. Our study aimed to explore the attitudes of people with early-stage dementia toward MAiD should it become accessible to them. Methods: We used a qualitative descriptive design consisting of eight face-to-face semi-structured interviews with persons living with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease, followed by a thematic analysis of the contents of the interviews. Results and Interpretations: Analysis revealed three main themes: 1) favourable to MAiD; 2) avoiding advanced dementia; and 3) disposition to request MAiD. Most participants anticipated dementia to be a painful experience. The main reasons for supporting MAiD were to avoid cognitive loss, dependence on others for their basic needs, and suffering for both themselves and their loved ones. Every participant said that they would ask for MAiD at some point should it become available to incompetent patients and most wished that it would be legal to access it through a request written before losing capacity. Conclusion: The reasons for which persons with Alzheimer’s disease want MAiD are related to the particular trajectory of the disease. Any policy to extend MAiD to incompetent patients should take their perspective into account.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Vincent Thériault, Diane Guay, Gina Bravo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The Canadian Journal of Bioethics applies the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License to all its publications. Authors therefore retain copyright of their publication, e.g., they can reuse their publication, link to it on their home page or institutional website, deposit a PDF in a public repository. However, the authors allow anyone to download, reuse, reprint, distribute, and/or copy their publication, so long as the original authors and source are cited.















_smaller.png)

