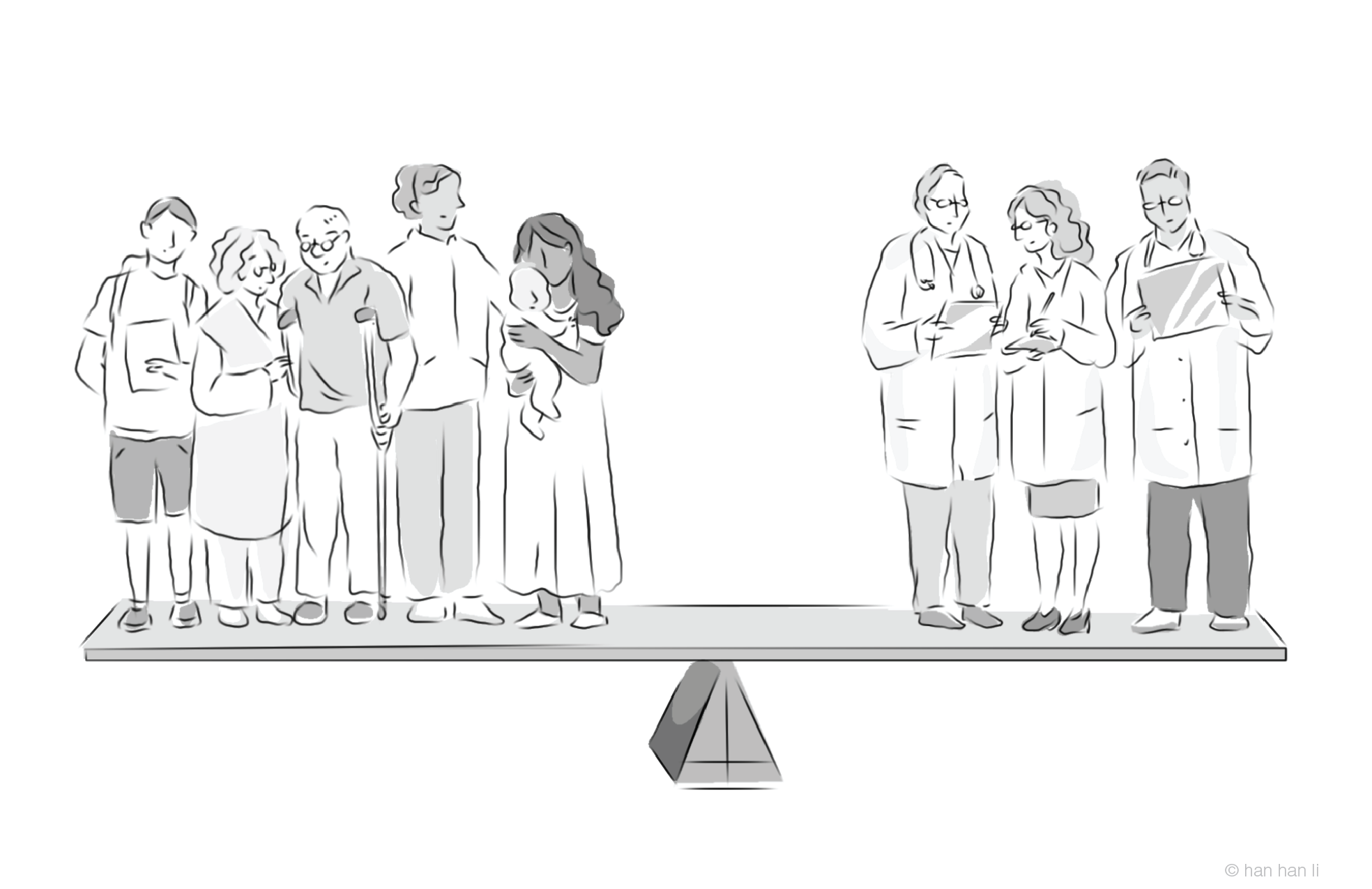
On Being an Ombudsman: Protecting the Public Interest While Navigating the Minefield of Policy Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7202/1092953arKeywords:
ombudsman, complainants, client, resolution, impartiality, policy networksLanguage(s):
EnglishAbstract
After 50 years of institutional history in Canada, the focus of ombuds has shifted from resolving individual complaints to improving the quality of government services for all. New tools in the ombuds world enabled the conceptualization and promotion of administrative fairness. Ombuds’ acquired expertise, which, shared with government, improved the delivery of services. Public systemic investigations are now seen as the ultimate expression of ombuds effectiveness. Consistent dialogue with public servants and organisational administrators inevitably links ombuds to policy networks. While informal links to policy networks can help ombuds resolve cases, they can also inadvertently create distance between ombuds and complainants. A former ombuds officer at Columbia University, Marsha Wagner emphasizes the importance of identifying systemic issues in ombuds practice, i.e., ombuds who do not focus on systemic issues may be derided as “wannabes”. This article suggests the pendulum has swung too far from the individual complainant to a systemic focus and urges caution in contemporary ombudship.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Daniel Johns, Brent Epperson

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The Canadian Journal of Bioethics applies the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License to all its publications. Authors therefore retain copyright of their publication, e.g., they can reuse their publication, link to it on their home page or institutional website, deposit a PDF in a public repository. However, the authors allow anyone to download, reuse, reprint, distribute, and/or copy their publication, so long as the original authors and source are cited.















_smaller.png)

